GraphQL is a data query language and runtime designed and used at Facebook to request and deliver data to mobile and web apps since 2012.
Build a simple GraphQL server
If you don’t have node js already installed you can Install & run your first application Nodejs. We start by making a folder for our application:
$ mkidr graph-server
$ cd graph-server
Install graphql, express and express-graphql.
$ npm install graphql
$ npm install express
$ npm install express-graphql
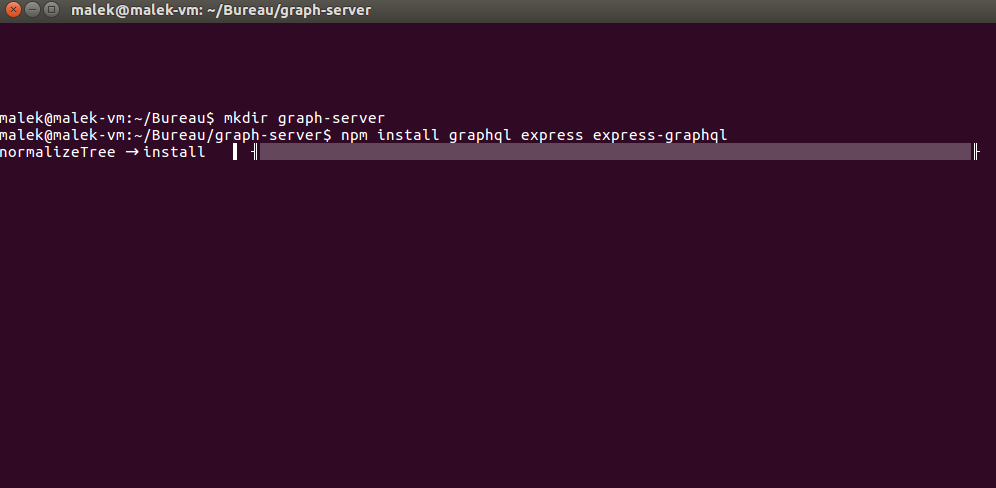
Create users.json Json file for Data
Create a file and name it users.json
{
"1": {
"id": "1",
"name": "Malekbenz",
"email": "[email protected]"
},
"2": {
"id": "2",
"name": "user",
"email": "[email protected]"
},
"3": {
"id": "3",
"name": "otheruser",
"email": "[email protected]"
},
"4": {
"id": "4",
"name": "Superuser",
"email": "[email protected]"
}
}
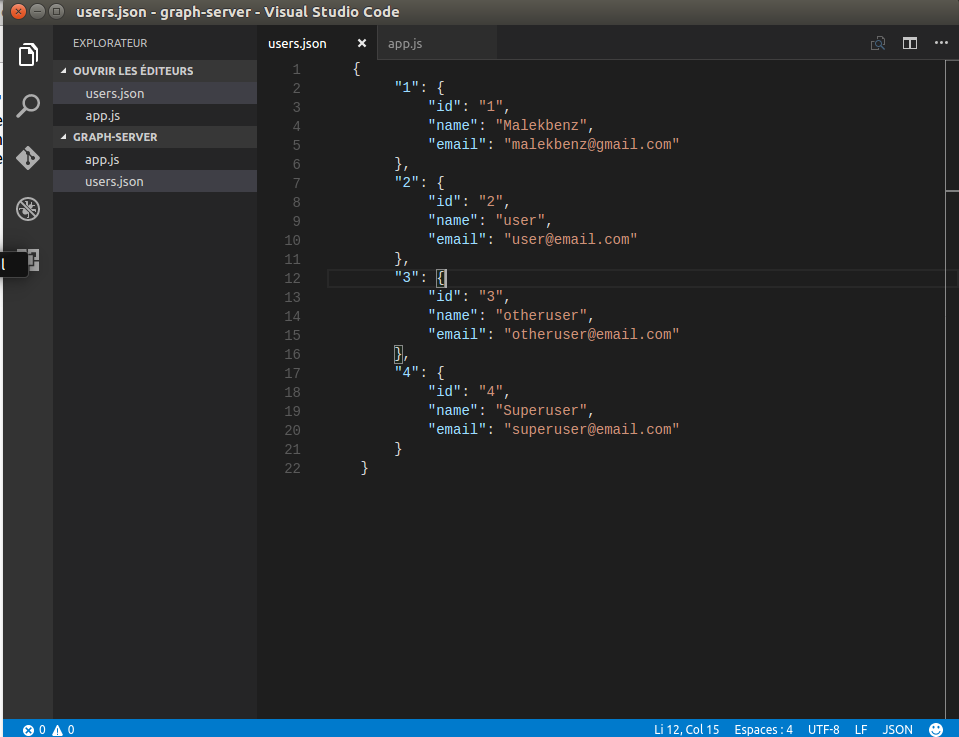
Create the Server
Create a file and name it app.js
var graphql = require('graphql'),
graphqlHTTP = require('express-graphql'),
express = require('express');
// Import the users file
var users = require('./users.json');
// Define the User type. The type of User is GraphQLObjectType
var userType = new graphql.GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'User',
fields: {
id: { type: graphql.GraphQLString },
name: { type: graphql.GraphQLString },
email: { type: graphql.GraphQLString },
}
});
// Define the schema with one top-level field, 'user', that
// takes an 'id' argument and returns the User with that ID.
var schema = new graphql.GraphQLSchema({
query: new graphql.GraphQLObjectType({
name: 'Query',
fields: {
user: {
type: userType,
// 'args' arguments that the 'user' query accepts
args: {
id: { type: graphql.GraphQLString }
},
// The resolve function take 'id' argument from above as a key
// to get the User from 'users'
resolve: function (_, args) {
return users[args.id];
}
}
}
})
});
express()
.use('/graphql', graphqlHTTP({ schema: schema, pretty: true }))
.listen(3000);
console.log('Server running on http://localhost:3000/graphql');
Save the file and run the application
$ node app.js
The server is running at localhost:3000/graphql. If you navigate to this address you will receive this notice:
{
"errors": [
{
"message": "Must provide query string."
}
]
}
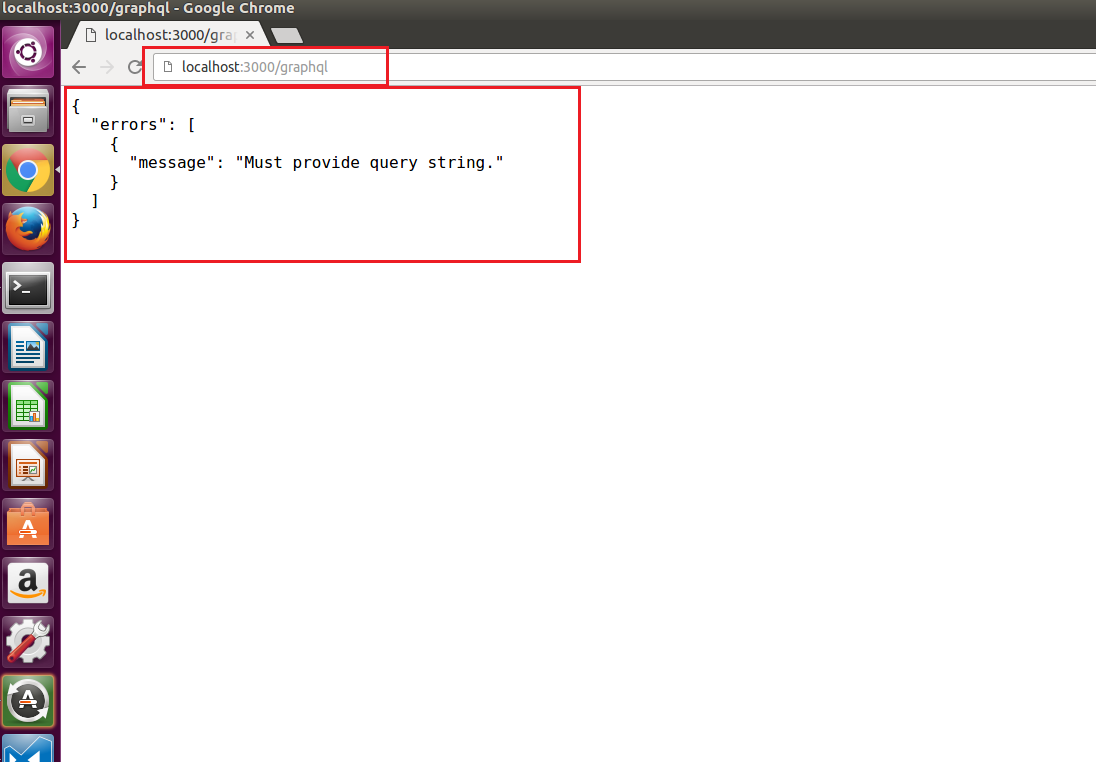
This message indicate that we need to provide a query.
Using a Queries againste a schema
A query is a string interpreted by a server that returns data in a specified format. Here is an example query:
Query:
{
user(id: "1") {
name
}
}
Result:
{
"data": {
"user": {
"name": "malekbenz"
}
}
}
Query:
{
user(id: "2") {
name,email
}
}
Result:
{
"data": {
"user": {
"name": "user",
"email":"[email protected]"
}
}
}
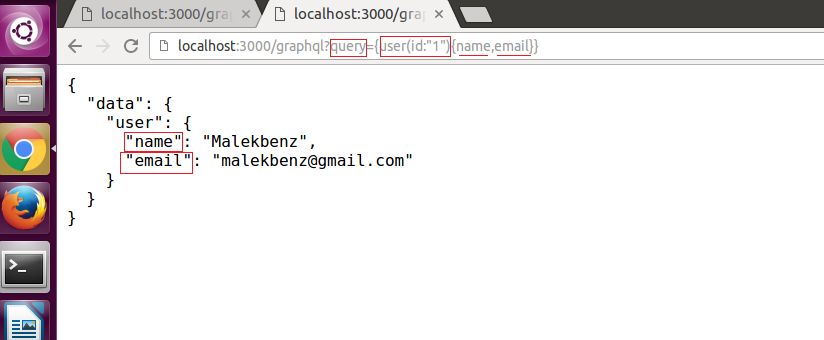
You can edit the above query; the result will automatically update when you do. If you make a syntax mistake it will be underlined in red. Try replacing id: “1” with id: “2”; replace name with id or with name id.
Remove all the whitespace in the query: {user(id:"1"){name}} (whitespace is optional in GraphQL). You can send this to your server via a GET request with a URL query string: http://localhost:3000/graphql?query={user(id:”1”){name}} - the server should respond with
Congratulations! You’ve built your first GraphQL server. Try different queries, or changing the data, or even adding new fields to the schema.